Modes of Operation of Transistor
Modes of Operation of Transistor: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Common Base Configuration, Common Emitter Configuration & Common Collector Configuration in Transistors etc.
Important Questions on Modes of Operation of Transistor
A transistor is connected in CE mode in which collector supply is and the voltage drop across load resistance connected in the collector circuit is . If and , determine base current in milliampere.
For a transistor in CE mode, and voltage drop across which is connected in the collector circuit is . Find the base current in microampere.
In a common base circuit, a resistance of is connected in the collector base section. The voltage drop across it is . Find the base current if .
For given biasing circuit, if voltage across collector-emitter is and current gain is and base current is then determine the value collector resistance in ohm.
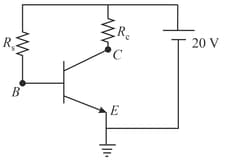
For given biasing circuit, if voltage across collector-emitter is and current gain is and base current is then determine the value collector resistance
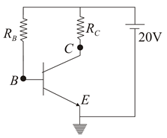
For a common-emitter transistor amplifier, the audio signal voltage across the collector resistance of is . What should be the value of in series with the supply of , if the base current is times the signal current in ,
To operate a transistor in active region, its emitter-base and collector-base junction respectively, should be
If the current gain of a common base circuit is , find the current gain of common emitter circuit.
The figure below shows, the transfer characteristics of a base biased transistor. Which of the following statement is true?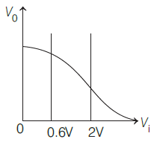
Draw the circuit arrangement and also explain the characteristics for a transistor in the common-emitter configuration. Also draw the curves and write the formula for voltage gain and current gain.
Current gain is maximum in the following configuration of a transistor:
In a common base transistor circuit, is the Output current and is the input current. The current gain is .........
The output characteristics of an transistor represent, ( - collector current, = potential difference between collector and emitter, = base current, = voltage given to base, = the potential difference between base and emitter)
Assertion: In a CE transistor amplifier the input current is much less than output current.
Reason: The common emitter transistor amplifier has very high input impedance -
A transistor, connected in common emitter configuration, has input resistance and load resistance of . If and an input signal is applied, find the power gain.
A change of in the emitter current brings a change of in the collector current. The values of are
A common emitter amplifier has a voltage gain of , an input impedance of and an output impedance of The power gain of the amplifier is
A common emitter amplifier has a voltage gain of 50, an input impedance of 100 and an output impedance of 200 The power gain of the amplifier is
A common emitter amplifier has a voltage gain of , an input impedance of and an output impedance of . The power gain of the amplifier is
An transistor in common emitter mode is used as a simple voltage amplifier with a collector current of . The positive terminal of a battery is connected to the collector through a load resistance and to the base through a resistance . For collector–emitter voltage , base–emitter voltage and base current amplification factor . Calculate the values of and .
